United We Stand: Industry and Famous Strikes
As the work of another school year begins, Labor Day reminds us to honor the nation's workers. Since the rise of industry, workers have used strikes and other forms of protest to demand change and recognition. Select the correct answer for each of the labor-related questions below.

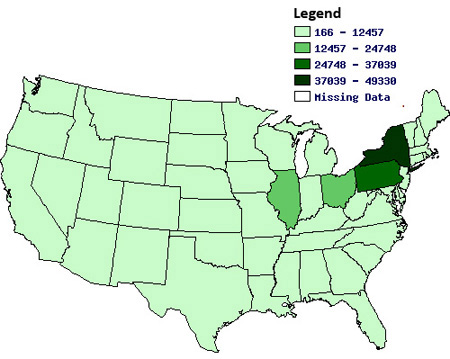
1. What U.S. census data does this map portray?
a. The 1930 relative concentration of "totally unemployed persons registered" in each state.
b. The 1870 relative amount of "total capital invested (in dollars) in manufacturing" in each state.
c. The 1920 relative concentration of "manufacturing establishments" in each state.
d. The 1950 relative concentration of "employed females" in each state.
By 1920, industry had established itself as a fixture of the American economy and way of life, though its hubs remained in the Mid-Atlantic. New York continued to be a center of industry, and Illinois, with the continuing rise of Chicago as an urban industrial center, had become one, as well.
2. On May 4, 1886, a peaceful workers' rally in Chicago's Haymarket Square ended in death and confusion when a dynamite bomb was thrown into a line of approaching police officers. The Haymarket Affair received nationwide media attention and the trials of the alleged guilty parties went all the way up to the U.S. Supreme Court. Four of the accused were hung and a fifth committed suicide.
What reform was the rally supporting?
a. The removal of hazardous parts-manufacturing machinery from a McCormick Harvesting Machine Company plant.
b. The passing of a minimum-wage law in the state of Illinois.
c. The paying of compensation to workers who suffered debilitating injuries from repetitive factory work.
d. The institution of the eight-hour workday.
The speakers at the Haymarket Affair supported strikers who had engaged in a May 1 nationwide walkout to support an eight-hour workday. On May 3, the first workday after the walkout, police killed two workers outside a McCormick plant during a confrontation between scabs (temporary workers hired to replace strikers) and strikers. This event provided an impetus for the Haymarket rally.
3. On February 6, 1919, more than 60,000 Seattle workers refused to work, marking the high point of a series of strikes and unrest that started in January 1919. The first labor action to effectively shut down an entire city, this strike hoped to secure what result?
a. The reinstatement of workers ousted by returning soldiers.
b. A pay raise for the city's shipyard workers.
c. The cessation of all U.S. hostilities against the Bolshevik Red Army in Russia and of any support for forces opposing the Red Army.
d. A stop to the installation of new machinery that would reduce the work force necessary in the shipyards.
During World War I, the government imposed wage controls, keeping the wages of Seattle shipyard workers down even as the shipyards expanded through war production contracts. Following the war, the workers expected a raise in their wages; when denied, approximately 25,000 members of the Metal Trades Council union alliance went on strike. A general citywide strike followed, with about 35,000 other workers striking in support of the shipyard protest. The strike officially ended on February 11—though not before touching off a widespread "Red Scare."
4. On December 30, 1936, the workers at Flint, Michigan's General Motors automobile plant began a six-week long strike to press for better working conditions. Organized by the United Auto Workers, the strike used what relatively unusual technique to make its point?
a. Strikers not only stopped working during the strike, but left town entirely, taking their families with them.
b. Strikers remained entirely silent during the strike.
c. Strikers, instead of picketing outside of the factory, occupied the factory, preventing upper management and law enforcement from entering.
d. Strikers sabotaged the factory's power supply, re-sabotaging it whenever plant management repaired it.
Known as the Flint Sit-down Strike, this strike used techniques later adapted by the civil rights movement. On December 30, workers sat down at their places and refused to leave the factory for six weeks. Provided food and supplies by supporters, the workers repelled attempts by the police to drive them out and even initiated the surprise takeover of another plant in the last two weeks of the strike.
 The map of the 1920 concentration of manufacturing establishments was generated by the University of Virginia Library's Historical Census Browser. The browser provides searchable census data for 1790 through 1960, with the option to visualize any data selections in maps such as the one above; all of the categories mentioned in Question One are categories available on the website. For Teachinghistory.org's review of the Historical Census Browser, go here.
The map of the 1920 concentration of manufacturing establishments was generated by the University of Virginia Library's Historical Census Browser. The browser provides searchable census data for 1790 through 1960, with the option to visualize any data selections in maps such as the one above; all of the categories mentioned in Question One are categories available on the website. For Teachinghistory.org's review of the Historical Census Browser, go here.
Teachinghistory.org's reviews the Library of Congress's American Memory collection Chicago Anarchists on Trial: Evidence from the Haymarket Affair, 1886-1887 here.
The Seattle General Strike Project looks at the 1919 general strike through primary sources, including photographs, video clips, newspaper articles, and oral histories. The website is part of the University of Washington's larger Seattle Civil Rights and Labor History Project, collecting primary sources on civil rights and labor movements throughout the city's history. NHEC reviews the Project here.
Historical Voices provides a website on the Flint Sit-down Strike: Remembering the Flint Sit-down Strike: 1936-1937. The website provides close to 100 oral history interviews with strikers, as well as essays on the events of the strike. NHEC's review of the website can be found here.
- Chicago (Ill.) Police Dept. Veterans of the Haymarket Riot, Parade banner of Veterans of the Haymarket Riot, 1895 (accessed July 27, 2009).
- Ulysses S. Grant, National Eight Hour Law: Proclamation, 1870 (accessed July 14, 2009).
- Library of Congress, Chicago Anarchists on Trial: Evidence from the Haymarket Affair, 1886-1887 (accessed July 14, 2009).
- Michigan State University, Historical Voices, Remembering the Flint Sit-down Strike (accessed July 14, 2009).
- University of Virginia Library, Historical Census Browser (accessed July 14, 2009).
- University of Washington, Seattle General Strike Project (accessed July 14, 2009).







 1915
1915 1925
1925 1917 (Note the military accents.)
1917 (Note the military accents.) 1905.
1905. 1935.
1935. 1910.
1910. 1940.
1940. 1895.
1895. 1955.
1955. 1960.
1960.
 [Question 1] The first photograph of either a president or a first lady broadcasting from the White House is of Mrs. Hoover. She began national broadcasts in 1929, even setting up a practice room in the White House where she could "improve [her] talkie technique." Many of her broadcasts were made from President Hoover's country retreat, Camp Rapidan, where she often devoted her programs to speaking to young people, urging girls to contemplate independent careers and boys to help with the housework. Mrs. Hoover had a degree in geology from Stanford University, as did her husband. She had accompanied him to China for two years, where he hadsupervised the country's mining projects. She later used the Mandarin Chinese she learned then to communicate with her husband privately when they were in the presence of others.
[Question 1] The first photograph of either a president or a first lady broadcasting from the White House is of Mrs. Hoover. She began national broadcasts in 1929, even setting up a practice room in the White House where she could "improve [her] talkie technique." Many of her broadcasts were made from President Hoover's country retreat, Camp Rapidan, where she often devoted her programs to speaking to young people, urging girls to contemplate independent careers and boys to help with the housework. Mrs. Hoover had a degree in geology from Stanford University, as did her husband. She had accompanied him to China for two years, where he hadsupervised the country's mining projects. She later used the Mandarin Chinese she learned then to communicate with her husband privately when they were in the presence of others. [Question 4] Julia Grant, although it happened after her husband was no longer president. Mrs. Grant went down the Big Bonanza silver mine in Virginia City, Nevada with her husband after hearing that he had wagered that she would be afraid to go. The Grants, along with their son, Ulysses, Jr., visited the mine on October 28, 1879, more than two years after Grant had left office. The mine's fabulous production of silver during the Civil War had done much to undergird the Government's financial credit internationally. Lucy Hayes later descended into the same mine with her husband, President Rutherford Hayes. On May 21, 1935, Eleanor Roosevelt made the national news by visiting the Willow Grove coal mine in Bellaire, Ohio, to observe the working conditions of the miners.
[Question 4] Julia Grant, although it happened after her husband was no longer president. Mrs. Grant went down the Big Bonanza silver mine in Virginia City, Nevada with her husband after hearing that he had wagered that she would be afraid to go. The Grants, along with their son, Ulysses, Jr., visited the mine on October 28, 1879, more than two years after Grant had left office. The mine's fabulous production of silver during the Civil War had done much to undergird the Government's financial credit internationally. Lucy Hayes later descended into the same mine with her husband, President Rutherford Hayes. On May 21, 1935, Eleanor Roosevelt made the national news by visiting the Willow Grove coal mine in Bellaire, Ohio, to observe the working conditions of the miners. [Question 7] Lyndon Johnson, with his wife Lady Bird on one side and Jackie on the other, was sworn in aboard Air Force One less than two hours after JFK's assassination. The ceremony was delayed to wait for Jackie to arrive. The most famous photograph of the event has Jackie in the foreground, standing in a pink suit still stained with her husband's blood, with LBJ in the center with his hand upraised taking the oath, and with Lady Bird in the background.
[Question 7] Lyndon Johnson, with his wife Lady Bird on one side and Jackie on the other, was sworn in aboard Air Force One less than two hours after JFK's assassination. The ceremony was delayed to wait for Jackie to arrive. The most famous photograph of the event has Jackie in the foreground, standing in a pink suit still stained with her husband's blood, with LBJ in the center with his hand upraised taking the oath, and with Lady Bird in the background.

 The University of Georgia's
The University of Georgia's 
