Local War Stories: Theodore Akimoto
World War II veteran Theodore Akimoto shares his personal memories of the war.
The audio from this clip is available independently as a MP3 file.
World War II veteran Theodore Akimoto shares his personal memories of the war.
The audio from this clip is available independently as a MP3 file.
World War II veteran Susumu Ito talks about his memories of serving in the all-Japanese-American 442nd Regimental Combat Team during the war and the internment of his parents in an American internment camp. The presentation includes film footage, images, and subtitles.
World War II veteran Mary Ginnerty shares her personal memories of the war.
The audio of this oral history is available independently as a MP3 file.
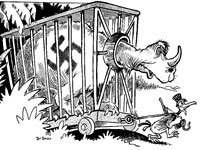
Dr. Seuss (Theodor Seuss Geisel), the prolific and talented children's book author, was also a political cartoonist. From 1941 to 1943, Seuss drew over 400 editorial cartoons as the chief editorial cartoonist for the New York newspaper PM. All 400 of his cartoons have been scanned onto this website by the staff of the Mandeville Special Collection Library at the University of California, San Diego, which houses the original cartoons in the Dr. Seuss Collection.
The cartoons are primarily related to issues surrounding World War II; and include caricature images of political figures like Adolph Hitler, Benito Mussolini, and Franklin D. Roosevelt. There are also a series of 10 War bond cartoons that Seuss drew for PM.
The site has a brief (500-word) introduction that gives an overview of Seuss's life and career. Currently the images are accessible by the month and year of publication or by subject. The site is somewhat difficult to use because of the lack of keyword search, but it is still a rich resource for information on popular culture, politics, and the media during World War II.

On August 6, 1945, the United States dropped the first atomic bomb used in warfare on Hiroshima, Japan. On August 9, 1945, the second atomic bomb struck Nagasaki. This age of nuclear warfare began less than a month after the first test of the atomic bomb in the New Mexican desert, and Robert Oppenheimer, leader of the Manhattan Project, later recalled, "There floated through my mind a line from the Bhagavad-Gita in which Krishna is trying to persuade the Prince that he should do his duty: 'I am become death: the destroyer of worlds.'"
The decision to use atomic bombs against Japan is considered among the most controversial decisions in military history. Multifaceted arguments examining the causes and effects of that decision began before the bombs fell, continued in the immediate aftermath, and have not yet ended, and we probe them from the perspectives of military, political, social, and cultural history. Was the bombing justified? Did it hasten the end of the war?
Primary and secondary educational resources support an emphasis on multiple perspectives and historical thinking in approaching units about Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The following suggestions are directed toward high-school and some middle-school classrooms.
Hot Topics: Hiroshima on the History News Network gives educators an overview of historiography and arguments behind the bombing. Among them, Peter Kuznick, Associate Professor of History and Director of the Nuclear Studies Institute at American University, addresses past and present perspectives in The Decision to Risk the Future . . . Harry Truman, the Atomic Bomb and the Apocalyptic Narrative. Sean Malloy, assistant professor of history at the University of California, Merced, Four Days in May . . . Henry L. Stimson and the Decision to Use the Atomic Bomb follows the political rationale and chronology leading to Hiroshima.
For students, Steven Mintz's Digital History essay, The Controversy Continues in the unit America at War: World War II, brings the discussion into the present day using argument about the presentation of an Enola Gay exhibit at the Smithsonian as a starting point to examine different points of view about Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Help students become familiar with the arguments and look for their own conclusions through materials digitized at the Truman Library. A special collection focuses on The Decision to Drop the Bomb and includes documents totaling almost 600 pages covering the years 1945-1964. Secondary source materials include an online version of Truman and the Bomb: A Documentary History, edited by Robert Ferrill. Among the primary source documents, the press release by Henry Stimson of August 6, 1945 includes an accompanying Lesson Plan for exploring the text and implications of that release.
The Gilder Lehrman Institute teachers' module on World War II incorporates a lesson plan on the Manhattan Project and a link to Was it Necessary?, a site highlighting this question and related primary documents exploring it.
The New York Times provides a lesson plan on He's the Bomb! with a look at Hiroshima 60 years later.
Edsitement Lesson Plans for grades 9-12 offer a balanced perspective on the decision to drop the bomb, linking to resources on the debates over the decision to bomb, Japan's decision to surrender, and arguments about the effect of the bombing on Japan's decision. Edsitement suggests assessment standards for its lessons and related resources for extending the lessons.
YouTube offers various historical footage of the bombing as well, but teachers will want to carefully screen videos and download them to a flash drive for accuracy and for age-appropriate coverage. And at the Library of Congress, a selected search of cultural collections and the Prints and Photographs online catalog also yields a multitude of photographs of the aftermath of the bombing and of further text-based resources.
The Hiroshima Peace Memorial Museum is a multifaceted look at the bombing and destructive effects on individuals and on the world. The museum presents a message of peace through a look at the horrors of war through survivor histories and exhibits on Hiroshima City and Japan before and after the atomic bombing. The museum directs many online materials toward elementary school ages, and is also well worth a visit from all ages for a conversation about how we remember, interpret, and use our historical past.
As Ronald Takaki writes in The Lessons of Hiroshima, "The history of this world-shattering event offers us lessons on war, race, leadership, reason, judgment, and the importance of cross-cultural understanding. Those who do not know history, a philosopher warned, will be doomed to repeat it. Hiroshima is a past that is not even past, and we ignore it at our peril."

Note: Unpublished because annotation does not seem to match website. Larger parent website also already covered at http://teachinghistory.org/history-content/website-reviews/23319.
This exhibit by an art student begins with 11 color postcard-like recreations of original black-and-white photographs documenting life in the Poston (AZ) War Relocation Center, where more than 17,000 Japanese-Americans were interned between 1942 and 1945 by the U.S. military. An accompanying essay provides background information and a brochure describes the Poston Monument. In addition, viewers can access six pages from "an Internment Camp's High School Yearbook," and additional legal documents, memoirs, newspaper and journal articles, a timeline, and book excerpts through links to 26 related documents and 40 websites. An important site on the internment experience.

My cousin sent me this, is it accurate?
"The first German serviceman killed in WW II was killed by the Japanese (China, 1937), the first American serviceman killed was killed by the Russians (Finland 1940); the highest ranking American killed was Lt Gen Lesley McNair, killed by the US Army Air Corps. So much for allies."
This question is a little more complicated than it appears on the surface. For instance, Germany and Japan were not formally allied in 1937 (the Tripartite Pact allying Germany, Japan, and Italy went into effect in September 1940), and the 1937 action in China predated by two years Germany’s 1939 entry into World War II.
Likewise, historians usually consider the Winter War fought between Russia and Finland from 1939 to 1940 separate from the Second World War; in any case, it occurred well before the United States and Russia were allied, which did not occur until December 1941. (At the time of the Winter War, Russia and Germany had signed a non-aggression treaty and would remain in a state of uneasy neutrality until the German invasion of the Soviet Union in July 1941).
Lieutenant General Lesley McNair was indeed killed by United States Army Air Force bombs in July 1945 as part of Operation Cobra, the breakout from the Normandy beachheads following the June 6, 1944, D-Day invasion. Along with Lieutenant General Simon Bolivar Buckner (killed by Japanese fire on Okinawa in 1945), General McNair was the highest-ranking American officer killed during the war.
In a larger sense, the question speaks to the confusion and chaos that forms an inevitable part of battle, and to the mistakes that confusion creates. Fratricide (the accidental targeting of friendly soldiers) has bedeviled armies for centuries. The development of gunpowder and firearms, which increased the distance between forces on the battlefield and thus expanded the chances for miscommunication, misidentification, and mistargeting in combat, increased the incidences of battlefield fratricide.
The advent of long-range artillery and air power in the 20th century created still more opportunities. So-called “friendly fire” episodes reflect not soldiers’ incompetence, carelessness, or treachery but the impossibility of determining precisely what is going on and who is who in the lethal and confusing environment of battle. In the 19th century, the Prussian military theorist Carl von Clausewitz termed this confusion and ambiguity the “fog of war,” and it constitutes an unavoidable part of warfare.
Military history features many famous instances of fratricide. Confederate General Thomas J. Jackson was shot by friendly pickets as he reconnoitered after the battle of Chancellorsville in 1863. In May 1940, three German bombers attempting to strike a French airfield became lost and instead bombed the German city of Freiburg by accident.
Scores of American GIs during the Second World War wrote of being strafed by American or British aircraft, being the targets of their own artillery shells (often fired from miles behind the front), or accidentally receiving fire from adjacent friendly units. Increasing distance between combatants, the impossibility of perfect communications, and more frequent actions at night have all made distinguishing friend from foe more difficult.
Amidst the chaos and terror of combat, even the most capable and well-intentioned soldiers sometimes mistakenly target their own troops. Nor have technological innovations such as night-vision goggles and precision munitions eliminated the threat of fratricide in combat. The 2004 death of Army Ranger and former NFL player Pat Tillman during a firefight in Afghanistan from rounds fired by fellow American soldiers is perhaps the best-known recent example.
Geoffrey Regan, Blue on Blue: A History of Friendly Fire, New York: Avon Books, 1995.
Charles R. Shrader, Amicicide: The Problem of Friendly Fire in Modern War, Ft Leavenworth, KS: Combat Studies Institute, US Army Command and General Staff College, 1982.
Richard Townshend Bickers, Friendly Fire: Accidents in Battle from Ancient Greece to the Gulf War, London: Leo Cooper Books, 1994.
"Major General Omar N. Bradley and Lieutenant General Lesley J. McNair during the recent maneuvers of the the Third Army in Louisiana. General Bradley is seen pointing out one ot the maneuver situations to General McNair," 1942, Prints and Photographs Division, Library of Congress.

I recently read that, prior to the bombing of Hiroshima in 1945, up to 1,000 Allied POWs were dying per week at the hands of the Japanese. Is this true?
I have found no indication of this figure in the works of several historians who have written about the fate of Allied POWs in Japanese captivity.
Gavan Daws, in Prisoners of the Japanese: POWs of World War II in the Pacific, states, “Tokyo’s policy as of late 1944 was ‘to prevent prisoners of war from falling into the enemy’s hands,’” citing proceedings of the International Military Tribunal of the Far East and a research report of the Allied Translator and Interpreter Service Section as his sources. Drawing on a document in the National Archives dated February 26, 1945, entitled “Captured Japanese Instructions Regarding the Killing of POW,” of the Military Intelligence Division, Daws cites an entry in the journal of the Japanese headquarters at Taihoku on Formosa that called for “‘extreme measures’ to be taken against POWs in ‘urgent situations: Whether they are destroyed individually or in groups, or however it is done, with mass bombing, poisonous smoke, poisons, drowning, decapitation, or what, dispose of the prisoners as the situation dictates. In any case it is the aim not to allow the escape of a single one, to annihilate them all, and not to leave any traces.’”
Daws concludes, however, that with regard to carrying out the policy of killing POWs in various camps, “the picture was mixed.” In Palawan, in the Philippines, Japanese soldiers machine-gunned, clubbed, and bayonets 150 POWs trying to escape air raid shelters that the captors had doused with gasoline and lit. During the Battle of Manila in February and March 1945, guards at the camp at Bilibid left without harming the POWs.
Historian David M. Kennedy has summarized figures regarding the brutal treatment of American POWs by the Japanese. “Ninety percent of American prisoners of war in the Pacific reported being beaten,” Kennedy states. “More than a third died. Those who survived spent thirty-eight months in captivity on average and lost sixty-one pounds.”
After noting that 20 American POWs died as a result of the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima, according to Japanese military commanders, and that between one and three American prisoners may have been killed by the Japanese after the bombing, Richard B. Frank states, “The average number of Allied prisoners of war or civilian internees who died each day of the effects of captivity at the hands of the Japanese easily doubled this toll.”
In a radio broadcast on the night of August 9, 1945, hours after the U.S. dropped the second atomic bomb on Japan, President Harry S. Truman linked the use of the bomb to the treatment by the Japanese of American prisoners of war: “Having found the bomb we have used it. We have used it against those who attacked us without warning at Pearl Harbor, against those who have starved and beaten and executed American prisoners of war, against those who have abandoned all pretense of obeying international laws of warfare. We have used it in order to shorten the agony of war, in order to save the lives of thousands and thousands of young Americans.” In a letter two days later, Truman wrote, “nobody is more disturbed over the use of Atomic bombs than I am, but I was greatly disturbed by the unwarranted attack by the Japanese on Pearl Harbor and their murder of our prisoners of war.”
Gavan Daws, Prisoners of the Japanese: POWs of World War II in the Pacific (New York: William Morrow, 1994), 324-25.
David M. Kennedy, Freedom from Fear: The American People in Depression and War, 1929-1945 (New York: Oxford University Press, 1999), 813.
President, “Radio Report to the American People on the Potsdam Conference,” August 9, 1945, in John T. Woolley and Gerhard Peters, The American Presidency Project [online]. Santa Barbara, CA: University of California (hosted), Gerhard Peters (database). Available from World Wide Web: http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/ws/?pid=12165.
Harry S. Truman to Samuel Cavert, August 11, 1945, in Harry S. Truman and the Bomb: A Documentary History, ed. and commentary by Robert H. Ferrell (Worland, WY: High Plains Publishing Co., 1996), 72.
Van Waterford, Prisoners of the Japanese in World War II: Statistical History, Personal Narratives, and Memorials Concerning POWs in Camps and on Hellships, Civilian Internees, Asian Slave Laborers, and Others Captured in the Pacific Theater (Jefferson, NC: McFarland, 1994).
Bernard M. Cohen, and Maurice Z. Cooper, A Follow-up Study of World War II Prisoners of War (Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office, 1954).
Images:
"U.S. medical men are attempting to identify more than 100 American Prisoners of War captured at Bataan and Corregidor and burned alive by the Japanese at a Prisoner of War camp, Puerto Princesa, Palawan, Philippine Islands. Picture shows charred remains being interred in grave: 03/20/1945," National Archives and Records Administration, Washington, DC.
"A volunteer of the Red Cross Motor Corps, at the loading of the Gripsholm, painting the destination on boxes of clothing, food, etc., for prisoners of war in Japan and the Far East," Prints and Photographs Division, Library of Congress.

In 1942 President Franklin Roosevelt issued Executive Order 9066 authorizing the removal of more than 110,000 people of Japanese ancestry, two-thirds of whom were U.S. Citizens, into internment camps. This site, created for a class project at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, provides a gateway to brief essays and samplings of primary sources about the internment period from 1942-1945, a time line, oral histories, and photographs. There are links to 34 electronic essays and roughly 50 websites. Some of the more useful links are to the the National Archives and Records Administration, which documents the rights of American Citizens and actions of the Federal Government; the War Relocations Authority Camps in Arizona; the Museum of the City of San Franciso; the Japanese American Exhibit and Access Project; and Heart Mountain Digital Preservation Project. The site also contains personal reminiscences of life in the camp. Though many links on this site are useful for research on Asian-American history and the history of the World War II home front, this site should be used carefully. Some of the information presented as "fact" is highly controversial, some links present hearsay or speculation as fact, and several of the links are broken or obsolete.

This site provides access to the digitized resources of the Japanese American National Museum in Los Angeles.
Collections include more than 300 letters sent to Clara Breed, a San Diego librarian, by her former patrons after their relocation to internment camps; panoramic photos from Buddhist Churches of America events; artwork by Hideo Date, Hisako Hibi, Estelle Ishigo, Henry Sugomoto, and Benji Okubo; the diary of Stanley Hayami, a high school student during the internment years, later killed in combat at age 19; sketches and watercolors from the diary of George Hoshida; photographs of Manzanar and Tule Lake by Jack Iwata, as well as other photographs of daily life in the internment camps; a major collection of issei immigrant artifacts and plantation clothing; and photographs for the Rafu Shimpo, one of the oldest Japanese American newspapers in the U.S.
This is an excellent source for anyone seeking primary sources related to Japanese American experience in the U.S., particularly with an emphasis on the years of internment.